章節 7 Profit, Profit Margin and Profit/Loss Ratio
It’s one thing to make money trading and a different thing to keep the profits. The main problem on Forex, which most novel and experienced traders face, is the stability of earnings or consistent trading profit margin. Situations, where profits from forex trading fluctuating from zero to half the capital and sometimes turn into a loss, are familiar to everyone.
Profit vs. Profit Margin
Making a profit in a single trade is not an arduous task. However, that doesn't mean you're earning enough to survive for the long haul. The difference between profit and profit margin is that the profit margin gives you a better idea of your financial strength than profit alone. Because, even if your profits are substantial, your profit margin may be slim.
Profit is the amount your trade gains. It is a number that remains when you subtract loss from your revenue. You can find profit by looking at your trade's performance report. But profit alone can be deceiving.
Profit margin measures your trade's profits and helps you determine your success or failure. It is not an absolute value. Instead, it looks at what your trade's profits mean in the form of percentages or decimals. Profit margins provide a more realistic perspective.
The Importance of Profit Margin
The importance of profit margin is that it shows how much return you get from the money you're spending.
For example, Company A spends $900,000 to sell $1 million in products and services, generating $100,000 in profits. Company B spends $400,000 to generate $500,000. The two companies generate the same profit ($100,000), but are they equally profitable?
The simple answer is no. The more a company spends to generate a designated profit, the more vulnerable it is to minor cost shifts.
If you have a good profit margin, you're better equipped to ride out the inevitable fluctuations in loss and profit.
Profit/Loss Ratio
A profit/loss ratio refers to the size of the average profit compared to the size of the average loss per trade. For example, if your expected profit is $900 and your expected loss is $300 for a particular trade, your profit/loss ratio is 3:1 - which is $900 divided by $300. Many trading books and "gurus" advocate a profit/loss ratio of at least 2:1 or 3:1.
In forex, it’s quite easy to determine your profit-loss ratio - both in general and for each trade. To see how your forex account is treating you, simply divide your total gains over a certain period by the total number of winning positions you placed during that same time. Then divide your total losses by the number of losing positions. The ratio between your average wins per trade and your average losses per trade is your overall profit/loss ratio.
How to Set a Profit/Loss Ratio
It’s interesting to note that, although forex traders are correct in most of their trading predictions, they often end up losing more than they gain. The reason is simple - they make less on their winning positions, and they lose more on their losing ones.
When it comes to placing a trade, you should set your profit-loss ratio, as well. You do that by setting take profit and stop loss orders. The distance of each one of these from your strike price is that position’s profit-loss ratio.
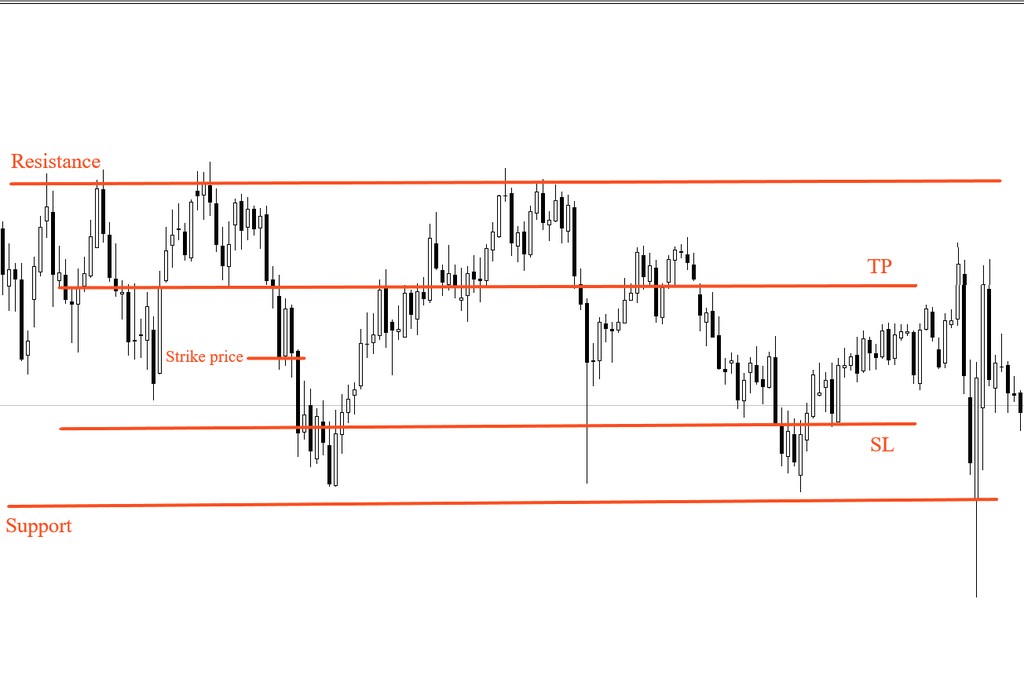
On the chart above, your base price is your strike price - that’s the value at which you opened your position minus the spread. Now you have to decide at what price you want to open the position. If you do so at the marked strike level, equidistant from your orders, your profit-loss ratio will be 1:1.




